ML-Driven Lead Allocation Guide
Introduction
Lead allocation is a critical component of sales processes, determining the success rate of conversions. The objective is to ensure leads are assigned to the best-suited salesperson, optimizing for conversion. In our quest for efficiency, we are transitioning from rule-based allocation to an ML-driven approach.
The Allocation Service will engage with the ML model by providing lead and user data. The ML model's output will then guide the Allocation Service in executing the allocation.
Distribution Method
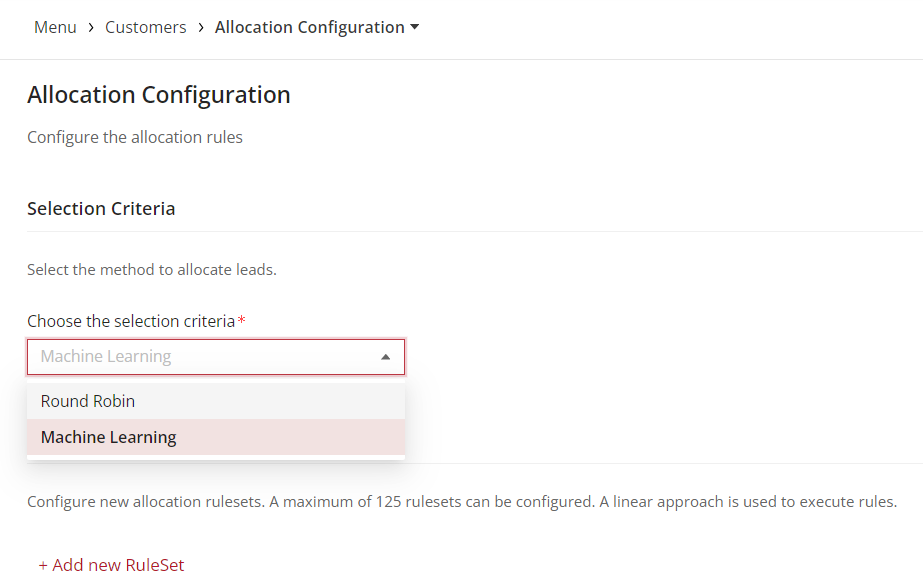
Before configuring the rule set, users must specify the distribution method:
-
Round-robin: The existing method where leads are equally distributed among users based on rule evaluation.
-
ML Model: A new method where after rule evaluation, the ML model determines the best-suited user for each lead.
Allocation Service Ruleset
Rules based on user and lead profiles can be set. However, the chosen distribution method dictates the rules:
-
Round Robin: No restrictions. Any lead or user attribute, including metrics like LCR, can be chosen.
-
ML Method: Only the "Open Lead Count" metric is allowed. This ensures clarity and avoids potential conflicts in results.
With the ML method, after initial rule-based shortlisting, the system sends lead and user details to the ML model. The model then returns the optimal user for each lead to the Allocation Service.
Machine Learning System
An external component, the ML system uses historical data and parameters like lead score to predict the best user for a set of leads. After analysis, it communicates its recommendations to the Allocation Service.
Step-by-Step Guide
-
Access the Vymo Web App: Start by logging in.
-
Navigate to Settings: Click on 'Self-serve', then 'Module Settings'. Next, select the relevant lead module.
-
Go to 'Allocation Configuration'.
-
Then from the dropdown, Select the method to allocate leads. By choosing either round-robin or machine learning.
See also
- Allocation Configuration