Lead Lifecycle Overview
What is the Lead Lifecycle?
The lead lifecycle represents the journey of a potential customer (lead) from the first point of contact with a business until conversion into a customer or exiting the sales funnel. It provides a systematic approach to managing and nurturing leads, crucial for increasing conversions, sales efficiency, and enhancing customer relationships.
Key Concepts
Lead
- Definition: An individual or organization interested in a product or service.
- Manifestation: Interest shown through actions like filling out a contact form, subscribing to a newsletter, or making an inquiry.
State
- Definition: Specific stage or status of a lead in the lifecycle.
- Common States: "New", "Assigned", "In Process", "Closed".
Transition
- Function: Movement of leads through different states, often triggered by actions or events like sales calls or missed appointments.
Allocation Rules
- Purpose: Predefined criteria to automatically assign leads to sales representatives based on factors like location, lead source, or product interest.
Reactivation
- Process: Reintroducing previously inactive or closed leads back into the sales funnel upon showing renewed interest.
Tags and Fields
- Function: Labels and data points for categorizing, filtering, and managing leads more efficiently.
States in Lead Lifecycle
- Representation: Distinct stages in a lead's journey, from "New" to "Assigned" to "Meeting Scheduled", culminating in "Won" or "Lost".
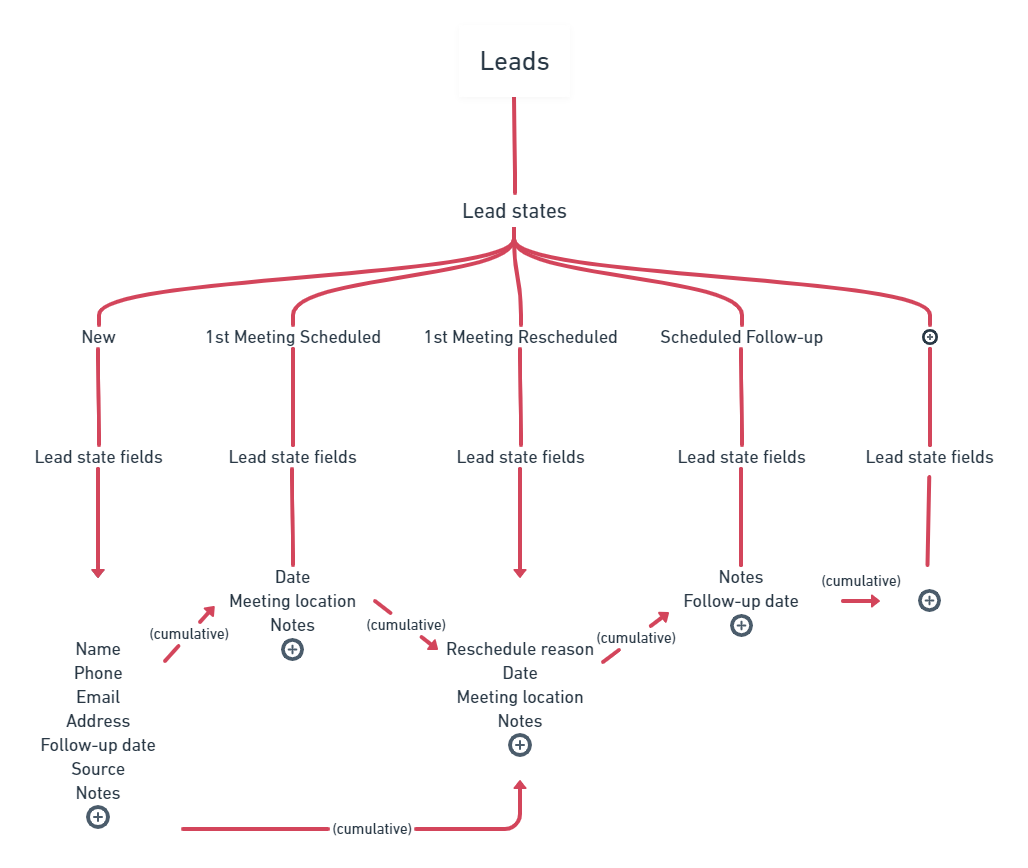
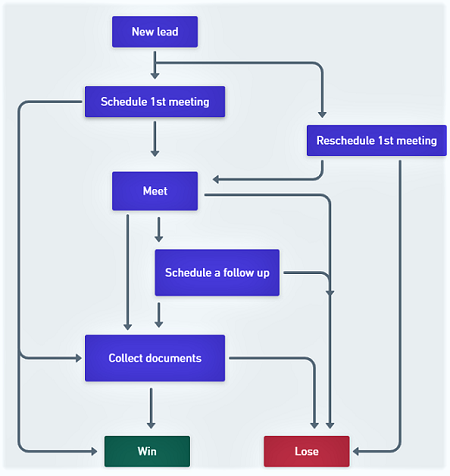
Usage of States
- Role: Essential elements in workflows, dictating the lead's journey through processes like scheduling calls or appointments.
Difference Between Metrics and Attributes
Attributes
- Definition: Characteristics or properties describing and categorizing leads, providing details like name, contact information, lead source.
- Purpose: Offer comprehensive view for segmentation, filtering, and organizing leads.
Metrics
- Definition: Quantitative measures or indicators of a lead's behavior, engagement, or progress.
- Purpose: Instrumental in evaluating lead management strategies, assessing conversion rates, response times, engagement levels.
Key Differences
- Nature: Attributes are descriptive and static, while metrics are dynamic and reflect evolving interactions.
- Type of Information: Attributes offer qualitative details, metrics provide quantitative data.
- Use Cases: Attributes for lead segmentation and profiling; Metrics for performance evaluation and optimization.
Example
- Attribute: Lead Name, Lead Source, Industry.
- Metric: Conversion Rate, Response Time, Engagement Score.
See also
- Lead Lifecycle
- Lead Lifecycle Overview
- How to create a leads module from a template
- How to create lead states
- How to add tags to lead states
- How to create transitions for lead states
- How to configure the state fields for leads
- How to enable or disable lead states
- How to enable or disable lead reassignment
- How to reactivate closed leads
- How to configure lead allocation rules
- How to specify the role permissions for the lead modules
- How to configure the lead reactivation behavior